다형성과 다형성을 사용하는 이유
1. 다형성(polymorphism) 이란?
- 하나의 코드가 여러 자료형으로 구현되어 실행되는 것
- 같은 코드에서 여러 다른 실행 결과가 나오는 것
- 정보은닉, 상속과 더불어 객체지향 프로그래밍의 가장 큰 특징 중 하나!
- 다형성을 잘 활용하면 유연하고/확장성있고/유지보수가 편리한 프로그램을 만들수 있음
package ch06;
class Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
}
class Human extends Animal{
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.println("사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.");
}
public void readBook() {
System.out.println("사람이 책을 읽습니다.");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal{
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.");
}
public void hunting() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 사냥을 합니다.");
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal{
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 날아 다닙니다.");
}
public void flying() {
System.out.println("독수리가 양 날개를 쭉 펴고 날아다닙니다.");
}
}
public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal hAnimal = new Human(); //여러 클래스를 Animal 타입으로 핸들링중
Animal tAnimal = new Tiger();
Animal eAnimal = new Eagle();
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.moveAnimal(hAnimal);
test.moveAnimal(tAnimal);
test.moveAnimal(eAnimal); //전부 Animal 타입이니, 상위 클래스로 형변환이 된다.
}
public void moveAnimal(Animal animal) {
animal.move(); //코드는 한 줄인데, 어떤 인스턴스 형이 들어갔느냐에 따라 move()의 implementation이 달라진다.
}
}상속->상속에서 오버라이딩->형 변환
Animal hAnimal = new Human();
Animal tAnimal = new Tiger();
Animal eAnimal = new Eagle();
상속을 하면, 하위클래스들을 상위 클래스 타입 하나로 모두 핸들링할 수 있다.
하지만,
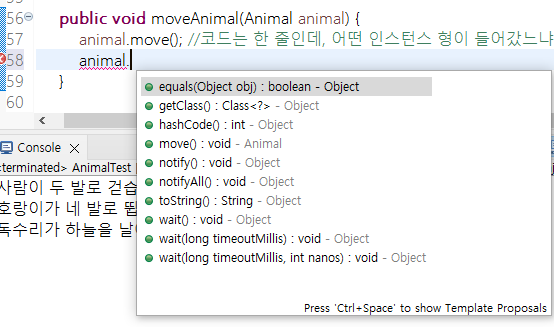
이 타입으로는 Tiger 클래스의 hunting()이나, Eagle의 flying() 메소드는 사용할 수 없다.
그러므로 다시 다운캐스팅을 해야한다.
공통적으로 쓰일 수 있는 메서드는 상위 클래스에 선언해놓자!
그럼 하위클래스 모두가 그 메서드를 쓸 수 있다.
class Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
public void eating() { //하위클래스들아 쓰거라
}
}
여기서 다형성은,
다른 클래스들이 한꺼번에 마치 동일한 타입으로 보이지만,
실질적인 임플리멘테이션은 각각 다르게 나타난다는 것을 말한다.
세 동물들을 ArrayList에 다 넣어버리자~!
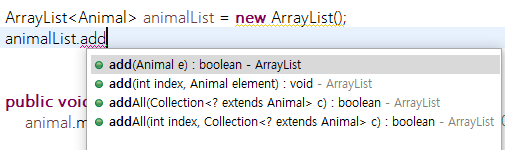

for문도 한 줄이지만, 어떤 animal이냐에 따라 임플리멘테이션이 각각 다르게 나타난다.
이게 바로 다형성!
2. 다형성을 사용하는 이유?
- 다른 동물을 추가하는 경우
- 상속과 메서드 재정의를 활용하여 확장성 있는 프로그램을 만들 수 있음
- 그렇지 않는 경우 많은 if-else if문이 구현되고 코드의 유지보수가 어려워짐

- 상위 클래스에서는 공통적인 부분을 제공하고 하위 클래스에서는 각 클래스에 맞는 기능 구현
- 여러 클래스를 하나의 타입(상위 클래스)으로 핸들링 할 수 있음
3. 다형성을 활용한 멤버십 프로그램 확장
일반 고객과 VIP 고객 중간 멤버십 만들기
고객이 늘어 일반 고객보다는 많이 구매하고 VIP보다는 적게 구매하는 고객에게도 해택을 주기로 했다.
- GOLD 고객 등급을 만들고 혜택은 다음과 같다
- 제품을 살때는 10프로를 할인해준다
- 보너스 포인트는 2%를 적립해준다
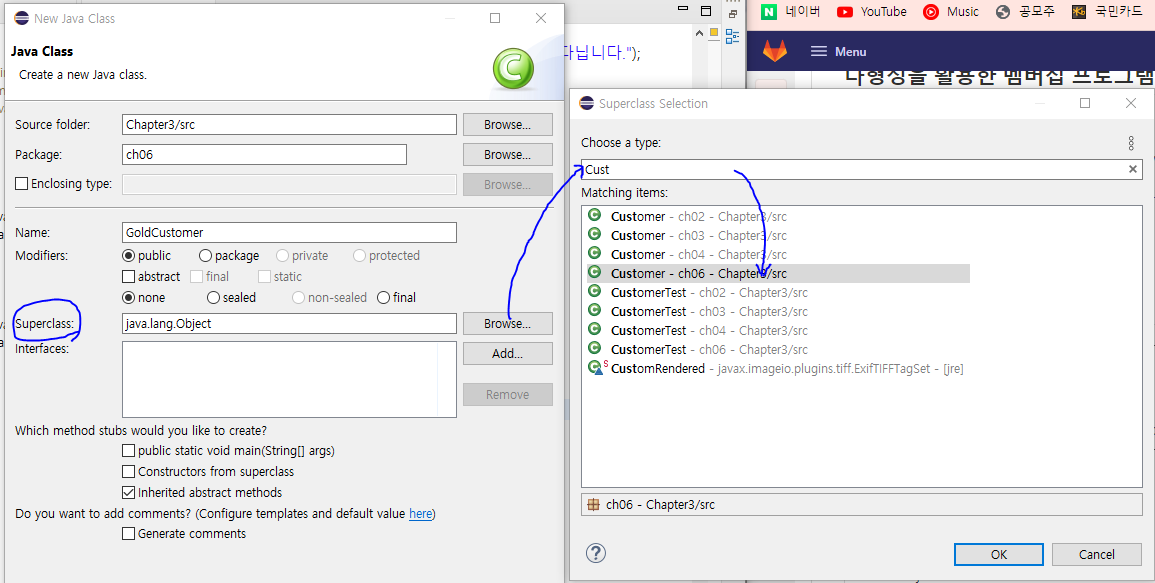
package ch06;
public class GoldCustomer extends Customer {
double salesRatio;
public GoldCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
salesRatio=0.1;
bonusRatio=0.02;
customerGrade="GOLD";
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint+=price*bonusRatio;
return price-(int)(price*salesRatio);
}
}
package ch06;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Customer> customerList = new ArrayList();
Customer customerT = new Customer(10010,"Tomas");
Customer customerJ = new Customer(10020,"James");
Customer customerE = new GoldCustomer(10030,"Edward");
Customer customerP = new GoldCustomer(10040,"Percy");
Customer customerK = new VIPcustomer(10050,"Kim");
customerList.add(customerT); //ArrayList에는 순서대로 들어가니까..
customerList.add(customerJ);
customerList.add(customerE);
customerList.add(customerP);
customerList.add(customerK);
for(Customer customer:customerList) {
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo());
}
}
}
할인율과 보너스포인트도 알아보자
package ch06;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Customer> customerList = new ArrayList();
Customer customerT = new Customer(10010,"Tomas");
Customer customerJ = new Customer(10020,"James");
Customer customerE = new GoldCustomer(10030,"Edward");
Customer customerP = new GoldCustomer(10040,"Percy");
Customer customerK = new VIPcustomer(10050,"Kim");
customerList.add(customerT); //ArrayList에는 순서대로 들어가니까..
customerList.add(customerJ);
customerList.add(customerE);
customerList.add(customerP);
customerList.add(customerK);
for(Customer customer:customerList) {
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo());
}
int price=10000;
for(Customer customer:customerList) {
int cost=customer.calcPrice(price); //리스트의 한 고객씩 꺼내지며 계산이 된다
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName()+"님이 "+cost+"원 지불하셨습니다.");
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName()+"님의 현재 보너스 포인트는 "+customer.bonusPoint+" 입니다.");
}
}
}
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3-8.객체 지향 핵심 - 다운캐스팅, instanceof (0) | 2022.01.22 |
|---|---|
| 3-7.객체 지향 핵심 - 상속 (0) | 2022.01.21 |
| 3-5.객체 지향 핵심 - 메서드 재정의와 가상 메서드 원리 (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| 3-4.객체 지향 핵심 - 메서드 재정의(overriding, 오버라이딩) (0) | 2022.01.15 |
| 3-3.객체 지향 핵심 - 상속에서 클래스 생성 과정과 형 변환 (0) | 2022.01.15 |
