Spring
Spring Boot - Interceptor
개발자 김혜린
2022. 6. 20. 18:16

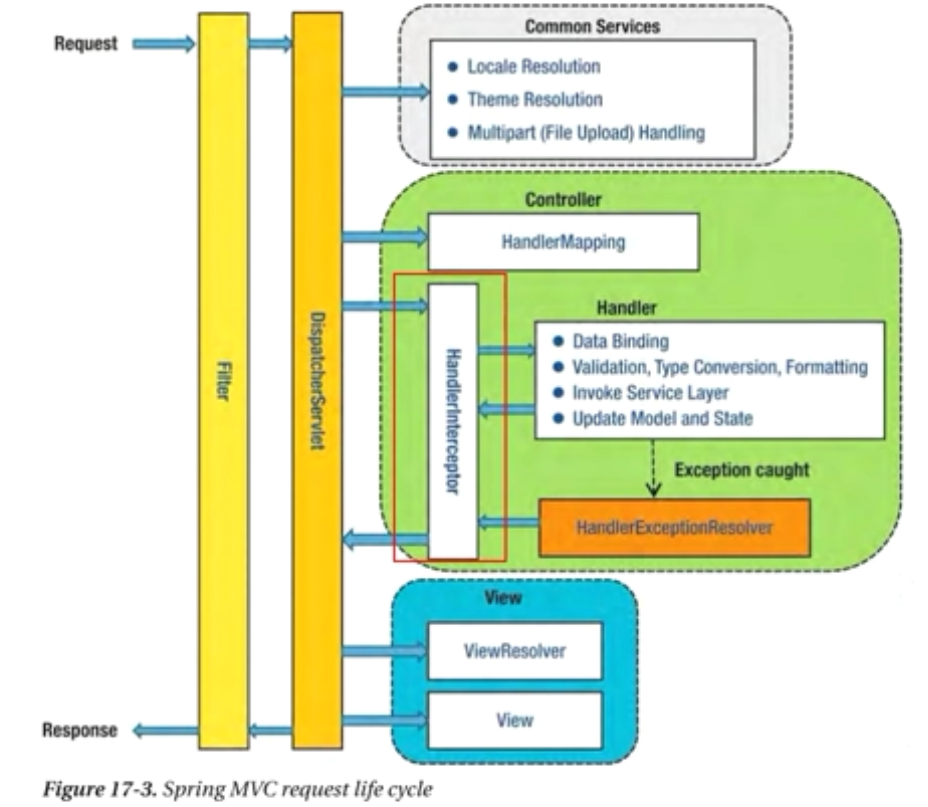
Filter는 Web application에 등록된다
package com.example.intercepter.intercepter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
return false;
}
private boolean checkAnnotation(Object handler, Class clazz){
//resource javascript, html
if (handler instanceof ResourceHttpRequestHandler){
return true;
}
//annotation check
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; //handlerMethod 객체를 만들기 위해 handler를 형변화시켰다
if(null !=handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(clazz) || null!=handlerMethod.getBeanType().getAnnotation(clazz)){ //MethodAnnotation에 class가 붙어있는가 or annotation이 달려있는가
// Auth annotation이 있으면 무조건 true
return true;
}
return false;
}
}

인터셉터가 동작하지 않으니,
인터셉터를 등록해주자
package com.example.intercepter.config;
import com.example.intercepter.intercepter.AuthInterception;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.client.support.BasicAuthenticationInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor //final로 선언된 객체들을 생성자에서 주입받을 수 있도록 해준다
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//@Autowired로 자기자신을 받을 수 있지만 순환 참조 생길까봐 @RequiredArgsConstructor 사용해서 생성자에서 주입받도록 함
private final AuthInterception authInterception;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterception);
}
}
package com.example.intercepter.controller;
import com.example.intercepter.annotation.Auth;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/private")
@Auth
@Slf4j
public class PrivateController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
log.info("private hello controller");
return "private Hello!";
}
}
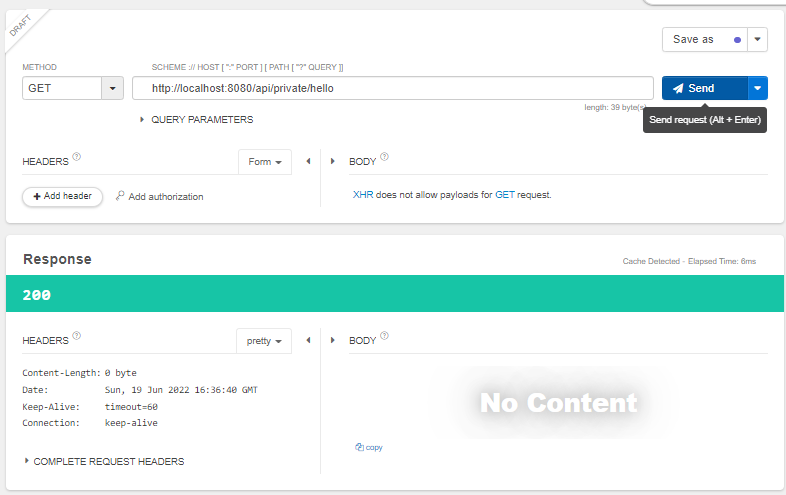
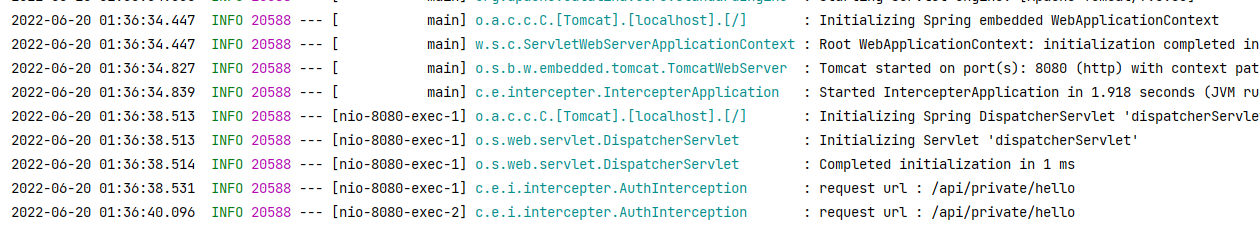
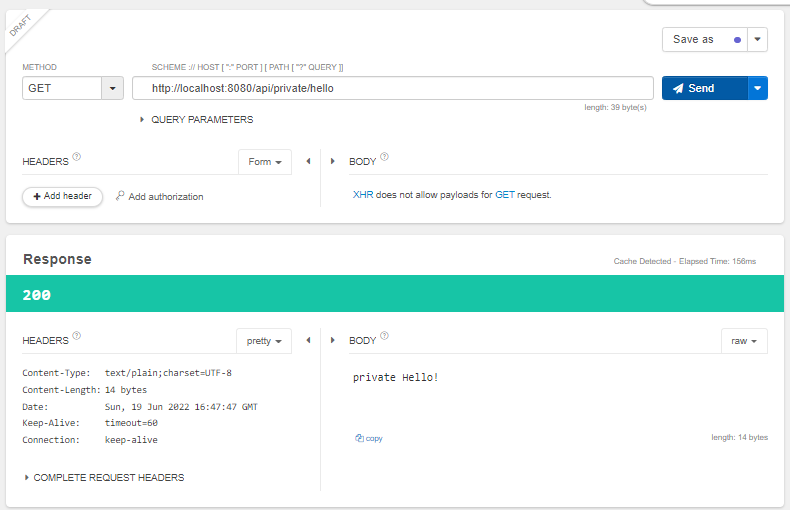
log.info("private hello controller");가 안찍혔다..
그 이유는?
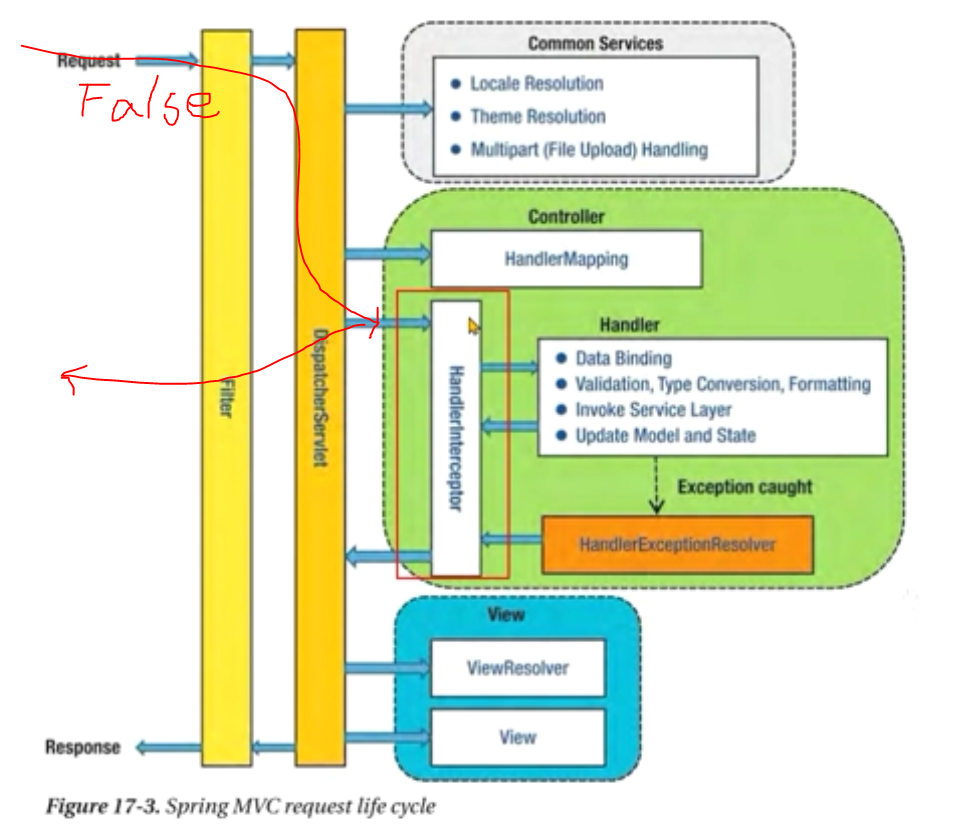
true여야만 Interceptor로 갈 수 있는데,
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
return false;
}에서 false를 리턴하고 있으니 들어갈 수가 없는것..
true로 바꿔주자
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
return true;
}
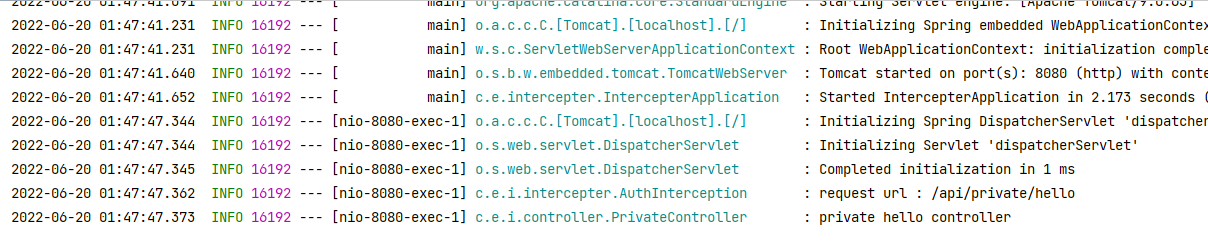
true가 되어야
interceptor를 넘어가
로직이 실행되는 것이고,
true가 아니라면 return이 된다.
이제 권한 체크를 해보자
package com.example.intercepter.intercepter;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
//권한 체크
boolean hasAnnotation = checkAnnotation(handler, Auth.class);
log.info("has annotation : {}", hasAnnotation);
return true;
}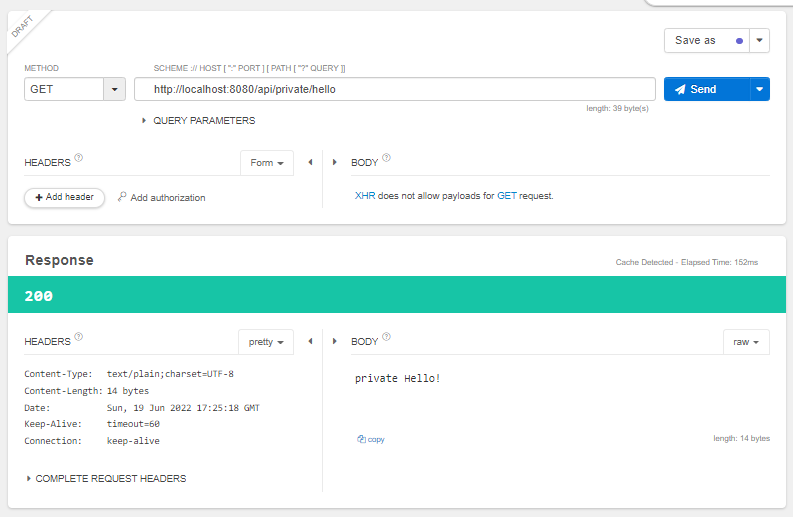

다르게 요청을 줘보면?
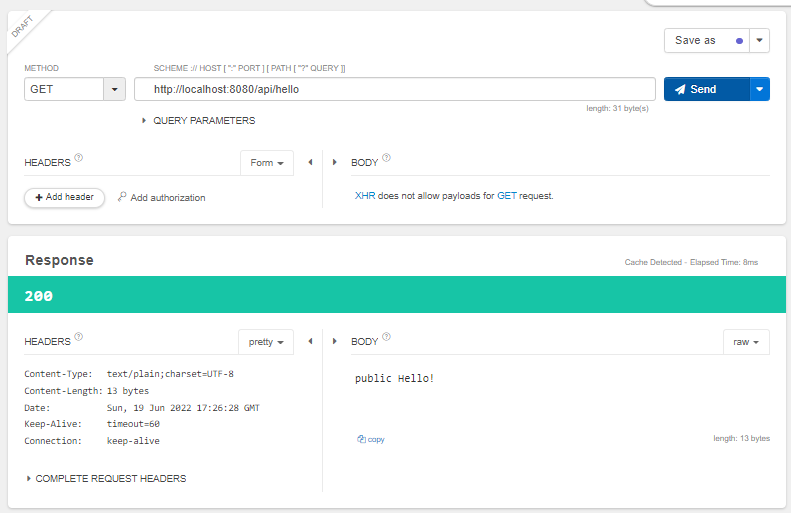

@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
//권한 체크
boolean hasAnnotation = checkAnnotation(handler, Auth.class);
log.info("has annotation : {}", hasAnnotation);
//나의 서버는 모두 public으로 동작을 하는데
//단! Auth 권한을 가진 요청에 대해서는 세션,쿠키를 볼 수 있다
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString(request.getRequestURI())
.query(request.getQueryString())
.build()
.toUri();
if(hasAnnotation){
//권한 체크
String query = uri.getQuery();
log.info("query : {}", query);
if(query.equals("name=steve")){ //쿼리가 steve일때만 통과
return true;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}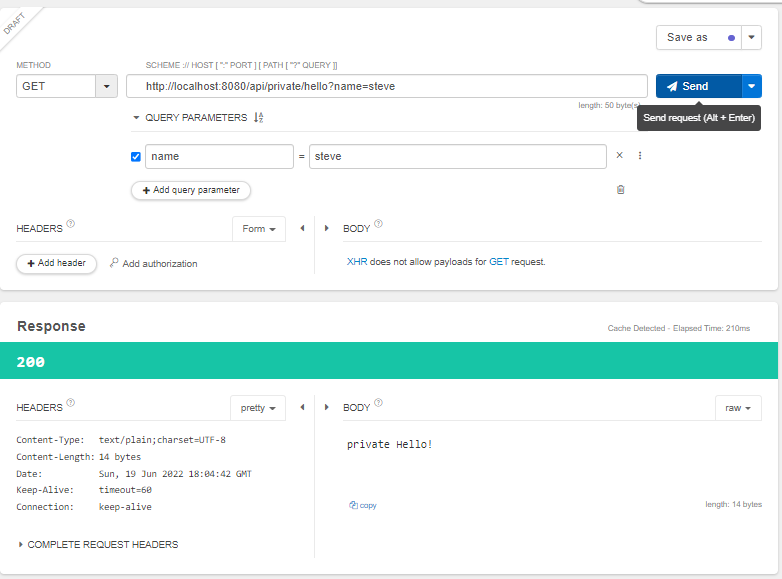
steve가 아닌 다른 값을 넣으면
동작하지 않음(Body에 아무 값도 안들어감)
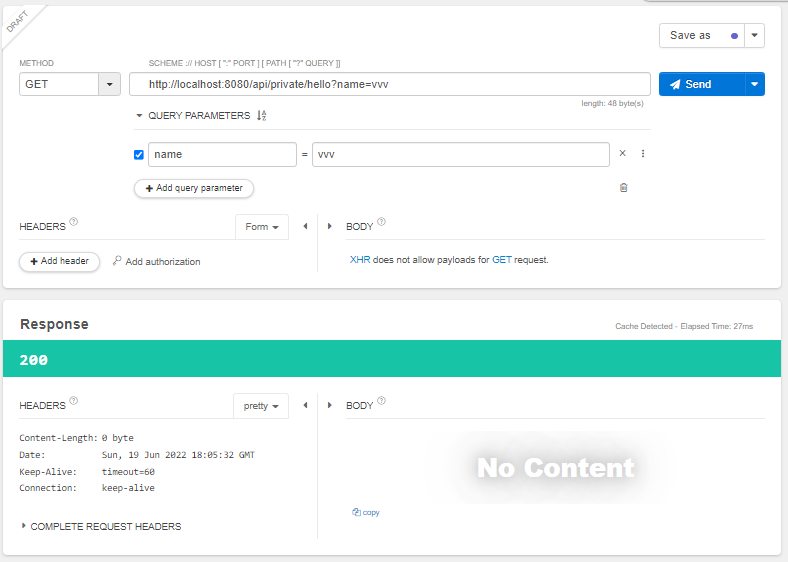
특정 URL만 검사하기
package com.example.intercepter.config;
import com.example.intercepter.intercepter.AuthInterception;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.client.support.BasicAuthenticationInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor //final로 선언된 객체들을 생성자에서 주입받을 수 있도록 해준다
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//@Autowired로 자기자신을 받을 수 있지만 순환 참조 생길까봐 @RequiredArgsConstructor 사용해서 생성자에서 주입받도록 함
private final AuthInterception authInterception;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterception).addPathPatterns("/api/private/*"); //"/api/private/*" 하위 아래 모든것만 검사하겠다.
}
}특정 URL 빼기
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterception).excludepathpatterns("/api/private/*");
}
그럼 아래와 같이
특정 어노테이션을 거치지 않아도 된다
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
//권한 체크
boolean hasAnnotation = checkAnnotation(handler, Auth.class);
log.info("has annotation : {}", hasAnnotation);
//나의 서버는 모두 public으로 동작을 하는데
//단! Auth 권한을 가진 요청에 대해서는 세션,쿠키를 볼 수 있다
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString(request.getRequestURI())
.query(request.getQueryString())
.build()
.toUri();
if(hasAnnotation){
//권한 체크
String query = uri.getQuery();
log.info("query : {}", query);
if(query.equals("name=steve")){ //쿼리가 steve일때만 통과
return true;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
1. Interceptor에서 @Auth가 붙은 클래스나 메소드를 검사한다던지 (메소드에다 붙이면 일관성이 떨어지기때문에 컨트롤러나 특정 URL에 매칭하는게 좋다)
2. Config에서 특정 주소를 검사하던지
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterception).addPathPatterns("/api/private/*"); //"/api/private/*" 하위 아래 모든것만 검사하겠다.
}예외 터뜨리기
package com.example.intercepter.exception;
public class AuthException extends RuntimeException{
}
package com.example.intercepter.intercepter;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthInterception implements HandlerInterceptor { //HandlerInterceptor 상속받기
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("request url : {}", url);
//권한 체크
boolean hasAnnotation = checkAnnotation(handler, Auth.class);
log.info("has annotation : {}", hasAnnotation);
//나의 서버는 모두 public으로 동작을 하는데
//단! Auth 권한을 가진 요청에 대해서는 세션,쿠키를 볼 수 있다
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString(request.getRequestURI())
.query(request.getQueryString())
.build()
.toUri();
if(hasAnnotation){
//권한 체크
String query = uri.getQuery();
log.info("query : {}", query);
if(query.equals("name=steve")){ //쿼리가 steve일때만 통과
return true;
}
//권한이 없으면
// return false; 가 아니라
throw new AuthException(); //throw시키자
}
return true;
}
package com.example.intercepter.handler;
import com.example.intercepter.exception.AuthException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
@RestControllerAdvice //이걸로 받아서
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(AuthException.class) //AuthException.class가 터지면
public ResponseEntity authException(){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED).build(); //HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED, 401을 내리겠다
}
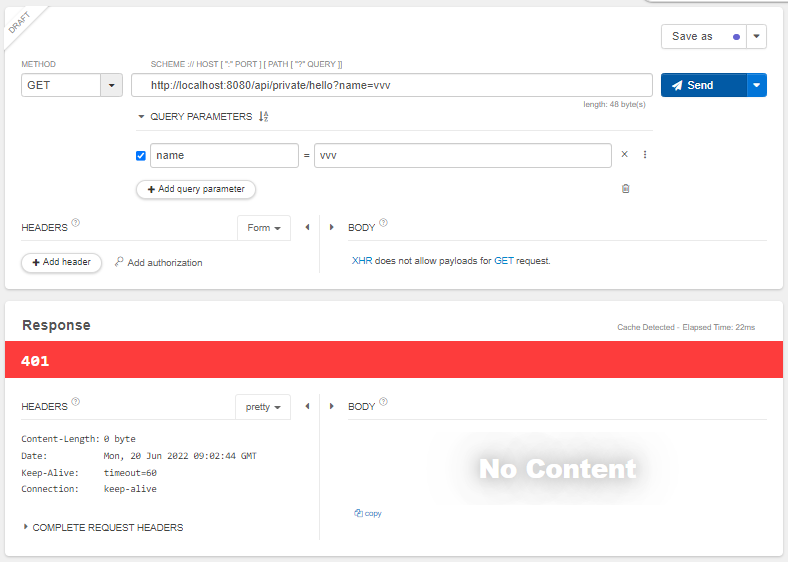
}
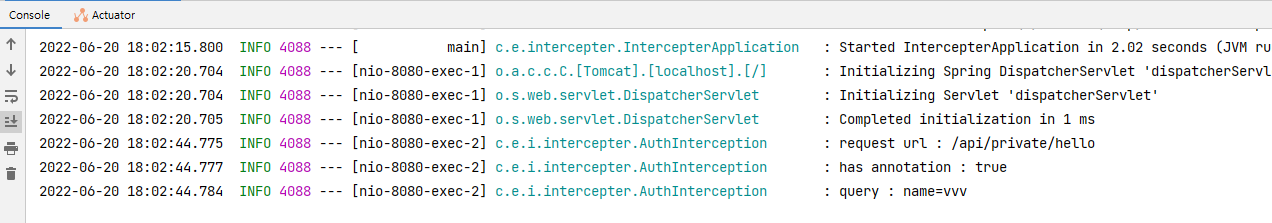
boolean hasAnnotation = checkAnnotation(handler, Auth.class); //스프링 context에서 관리중 (Filter는 이게 불가능)
log.info("has annotation : {}", hasAnnotation);
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor //final로 선언된 객체들을 생성자에서 주입받을 수 있도록 해준다
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//@Autowired로 자기자신을 받을 수 있지만 순환 참조 생길까봐 @RequiredArgsConstructor 사용해서 생성자에서 주입받도록 함
private final AuthInterception authInterception;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authInterception).addPathPatterns("/api/private/*"); //"/api/private/*" 하위 아래 모든것만 검사하겠다.
// registy.addInterceptor... 위의 코드가 끝나면 이 코드와 같이 다른 인증도 할 수 있음
}
}
Filter와의 차이점은
인터셉터는 스프링 컨텍스트에서 관리되고 있기 때문에
어노테이션이나 클래스로 활용 가능
Filter는 웹 어플리케이션에서 관리되고 있기 때문에
handler라는 오브젝트가 없다
궁금하면 handler 메소드를 찾아보자